What is it called when skin loses its pigment?
Hypopigmentation, which can happen for a number of causes, is the loss of skin pigment. We will look at the various forms of hypopigmentation, their causes, and available treatments in this piece.
DescribeHypopigmentation :
Melanin, the skin’s natural pigment, is lost in hypopigmented skin, a medical disorder. Our skin, hair, and eyes are all colored thanks to melanin. A decline in melanin production, harm to the melanocytes (cells that produce melanin), or the decomposition of the melanin pigment itself all contribute to hypopigmentation.
Hypopigmentation Types :

Hypopigmentation comes in a variety of forms, including:
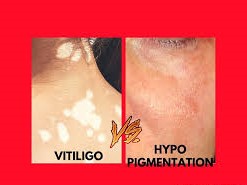
Vitiligo
Melanocytes are destroyed in vitiligo, causing the epidermis to become colorless. Any portion of the body may develop white patches of skin as a result of this.
Albinism
Albinism is a genetic disorder that causes the skin, hair, and eyes to completely or partially lack pigment. Albinos are more likely to develop skin cancer and have very light-colored skin, hair, and eyes.
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
Inflammation, injury, or trauma to the epidermis can lead to this kind of hypopigmentation. It may result from burns, psoriasis, or other diseases like eczema.
Tinea versicolor
This fungus infection results in hypo- or hyperpigmented patches of the epidermis. The chest, back, and arms can develop patches, which are typically lighter or darker than the adjacent skin.
Hypopigmentation Factors:
Depending on the kind of hypopigmentation, different factors can cause it. Several typical reasons include:imgres (1)
Genetic factors
An altered gene that impacts melanin synthesis is the genetic cause of albinism. Similarly to this, some types of hypopigmentation, like vitiligo, can run in families.
Autoimmune conditions
Hypopigmentation can occur when the defense system of the body attacks and destroys melanocytes. This is true for vitiligo as well as other inflammatory diseases like lupus and scleroderma.
Reasons for Hypopigmentation
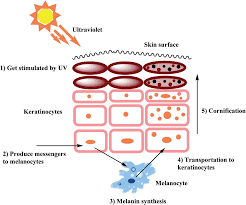
There are various causes of hypopigmentation, depending on the type. Among the common causes are:
Genetic influences
Albinism is genetically caused by a changed gene that affects melanin production. Similar to this, some hypopigmentation conditions, such as vitiligo, can occur in families.
Immune system disorders
when the body’s defense system targets and kills melanocytes, hypopigmentation can result. This is accurate not only for vitiligo but also for other inflammatory conditions like lupus and scleroderma.
Inflammation and injury
Inflammation, injury, or trauma to the epidermis can result in post-inflammatory hypopigmentation. Burns, cuts, and skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis are examples of this.
Fungal infections
A yeast-like fungus that inhibits the formation of melanin is the root cause of tinea vesicular.
Hyperpigmentation therapy
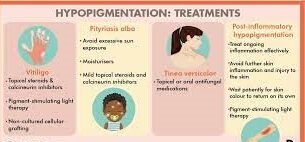
The cause of hypopigmentation will determine how the disease is treated. Hypopigmentation may not always need to be treated; instead, the skin may gradually revert to its natural color. The following are some typical therapies for those who wish to address the condition
Topical remedies
Corticosteroids, tacrolimus, and pimecrolimus are examples of topical remedies that can be used to soothe inflammation and encourage the formation of melanin in the skin.
Light treatment
The skin is exposed to ultraviolet light as part of light therapy, which can encourage the creation of melanin.
Surgical procedures
In some circumstances, pigmentation in the affected regions may be restored through the use of surgical procedures like skin grafts or melanocyte transplantation.
Cosmetics
To conceal hypopigmentation and even out skin tone, use cosmetics like self-tanners and makeup.
Hypopigmentation prevention
There are steps you can take to lower your chance of developing some types of hypopigmentation, even though some of them cannot be prevented. The following advice will help you avoid hypopigmentation:
Use sun protection
Exposure to sunlight increases your risk of getting hypopigmentation, especially in people who have albinism or vitiligo. Wear protective clothing and apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater to protect your skin.
Avoid skin damage
Skin damage frequently results in post-inflammatory hypopigmentation. Prevent injuries by wearing protective gear, exercising care when handling sharp objects, and staying away from potentially dangerous activities to lower your risk.
Take care of skin conditions
Eczema and psoriasis are two conditions that can make you more susceptible to post-inflammatory hypopigmentation. Manage these conditions and keep them under control with your doctor’s help to lower your chance.
Take care of your health
Some hypopigmentation types, like vitiligo, can be linked to other medical problems. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by consuming a balanced diet, working out frequently, and getting adequate rest to lower your risk.
Consult a doctor
If you observe any changes in your complexion, such as white patches or a loss of pigmentation, consult a doctor. Early detection and intervention can lessen the risk of complications and assist in preventing the condition from growing worse.
Conclusion:
The loss of the skin’s natural pigment is a disease known as hypopigmentation. Hypopigmentation comes in a variety of forms, each with unique reasons and therapies. The chance of developing hypopigmentation can be decreased by taking precautions to protect your skin from the sun, avoid skin injuries, treat skin conditions, maintain good health, and seek medical guidance. However, some forms of hypopigmentation cannot be prevented.


