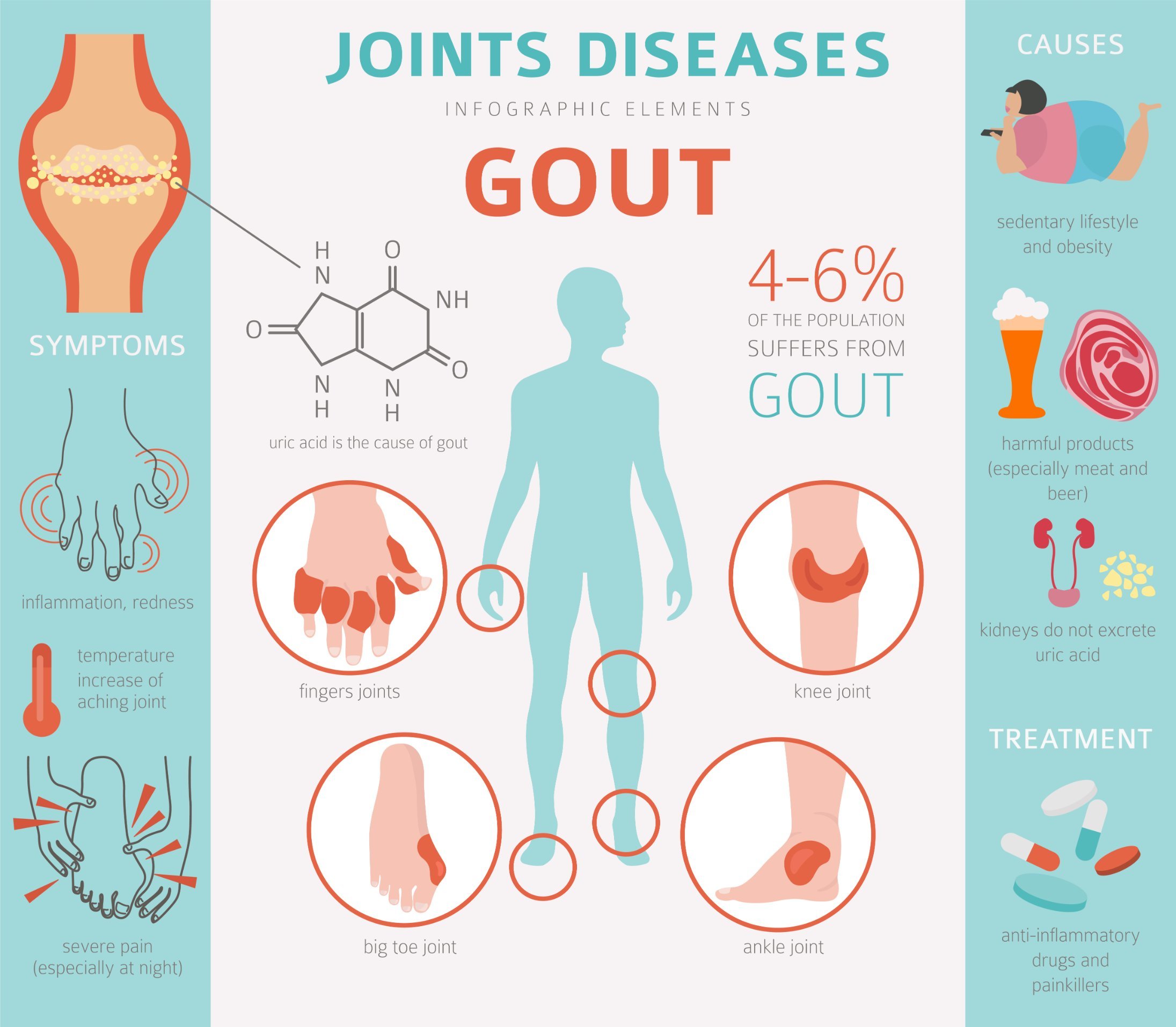
What is Gout:
Gout is a form of arthritis that develops when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, especially the major toe joint. These crystals cause inflammation, which results in the affected area swelling, turning red, and becoming excruciatingly painful. The presence of these uric acid crystals in the joints essentially causes an inflammatory response which is gout.
Historical Context and Prevalence:
The occurrence of gout in famous people’s lives, like those of King Henry VIII and Benjamin Franklin, dates back many centuries. Due to its connection to fatty foods, it was known as the “disease of kings” in historical jargon. Gout, however, is a common condition that affects people of all social classes. Gout still poses a serious health risk today and affects many people all over the world.
Importance of Awareness and Understanding:
Think about being presented with a challenging puzzle. It feels like a difficult assignment to solve if you don’t know how its components go together or how to put them together. Well, gout presents a similar issue as that puzzle. The cool aspect is that once you start discovering its secrets, you become a gout superhero. Understanding what causes gout enables you to exert control and lessen its effects. It’s similar to having a unique toolkit full of strategies for controlling gout. Therefore, consider awareness and comprehension to be your secret weapons. They assist you in navigating the gout’s twists and turns and guarantee the health and happiness of your joints
Causes and Risk Factors
Explanation of uric acid and its role
Gout, which is recognized as a unique kind of arthritis, develops as a result of a complex and delicate interplay among many contributing elements, with uric acid’s intricate role-playing a major role in its development. Uric acid is a naturally occurring byproduct that results from the breakdown of purines, a family of substances that are present in some meals and cellular structures. It normally takes on solubility in the bloodstream and is then eliminated by the renal routes. However, a stunning transformation occurs when uric acid levels exceed the body’s natural ability to digest them efficiently. The extra uric acid goes through an amazing transformation, crystallizing into unique forms, and settling in the joint spaces. A constellation of hallmark symptoms, including pain, inflammation, and obvious swelling, that are inextricably tied with the gout story emerge from this complex series of circumstances.
Primary Causes:
- Genetics: A major contributing component to gout predisposition is genetics. The body’s ability to metabolize uric acid can be affected by inherited differences, which can either increase production or decrease excretion. This genetic mosaic helps to explain the wide range of gout susceptibility.
- Dietary Decisions: Dietary factors are a significant contributor to gout. Purine-rich foods, such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and drinks high in fructose can raise uric acid levels. These purines’ breakdown catalyzes the buildup of uric acid, which may eventually result in crystalline deposition.
- Lifestyle Factors: Modern lifestyles marked by sedentary behaviors, binge drinking, and a high intake of sugary foods can combine to increase the risk of gout. Such actions disrupt metabolic processes, which affects how uric acid is handled and raises the possibility of crystal formation.
- Age and Gender: Men are more likely than women to get gout and the risk increases after puberty. Post-menopause is more likely to affect women. Age and gender are significant factors in uric acid dynamics because of age-related changes in hormonal rhythms.
Secondary Causes and Underlying Conditions:
- Kidney Dysfunction: The kidneys control the removal of uric acid. Any limitation, including chronic kidney illness or dehydration, might hinder the body’s ability to eliminate uric acid, which promotes the formation of crystals.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Hypertension and gout have complex relationships. Kidney function is hampered by high blood pressure, which also affects uric acid removal. In addition, high uric acid levels can make hypertension worse, creating a vicious cycle.
- Metabolic Syndrome: The constellation of metabolic syndrome components—obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal lipid levels—creates a conducive environment for gout development. These factors synergize to heighten uric acid accumulation.
- Drugs: Some drugs, like diuretics and low-dose aspirin, might affect uric acid levels and encourage gout. Management of gout risk requires a thorough understanding of medication-induced hazards.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Gout:
When gout starts to show up, it gives us some hints. Here’s what you might notice at the beginning:
Sudden Joint Pain (typically in the big toe):
Gout, a kind of arthritis, has an eye-catching first appearance: it frequently begins with an unexpected attack of severe pain, generally in the big toe. Consider a situation in which you are going about your everyday tasks when your big toe suddenly becomes a cause of great agony. This fast onset of pain is not progressive; it’s more like a shock that catches you off guard.
Consider the experience of walking and then suddenly feeling your toe throb or sting. Even a light touch might cause a strong, shooting sensation. This sudden and unexpected pain may cause you to change your activity reflexively in an attempt to relieve the agony.
As a result, simple tasks like walking or putting on shoes become difficult. Because of the severity of the discomfort, you may even favor the other foot to avoid putting undue pressure on the injured toe. This acute and severe joint pain is frequently used as an early warning indication that gout is present.
Given the particular character of this discomfort, it is advisable to be aware of such symptoms and consider getting medical advice. Consultation with a healthcare professional may help you gain a full awareness of the condition and pave the way for appropriate management techniques to alleviate pain and ensure joint well-being.
Swelling and inflammation:
In addition to the discomfort, the joint may seem swollen and red. When you touch it, it may feel warm and delicate. This is your body’s reaction to what’s happening within the joint.
Symptom Progression and Potential Complications:
Gout can not always affect just one joint. It may also opt to visit other locations. If gout is not treated, it can lead to the production of tophi, which are little crystal deposits surrounding the joints. These can cause joint pain and even distort its structure, making movement difficult.
-
Diagnosing Gout:
Identifying and confirming gout involves a systematic approach, employing a range of diagnostic tools. Here’s a breakdown of the methods used:
-
Physical Exam:
A qualified healthcare professional does a comprehensive physical examination of the afflicted joint. This exam comprises analyzing the look of the joint, feeling discomfort, noting any symptoms of inflammation (such as redness and warmth), and measuring its range of motion. The healthcare practitioner receives vital insights into the joint’s status by thoroughly assessing these elements and assisting in the diagnosis procedure.
-
Blood Tests (Uric Acid Levels):
Blood testing is critical in the diagnosis of gout. These tests determine the level of uric acid in the blood. Because uric acid crystals are characteristic of gout, elevated uric acid levels can suggest the existence of the ailment. Monitoring uric acid levels aids in the confirmation of the diagnosis and adds to the development of an appropriate management approach.
-
Imaging (X-rays, Ultrasound):
Modern imaging modalities, such as X-rays and ultrasound, improve diagnostic precision even more. X-rays highlight the presence of urate crystals within the afflicted joint, assisting in the visualization of joint damage caused by untreated or persistent gout. Ultrasound imaging provides real-time visualization of the joint, assisting in the detection of symptoms of inflammation, tophi development, and other gout-related alterations.
The combination of various diagnostic modalities yields a complete picture, allowing healthcare practitioners to effectively diagnose gout and personalize treatment measures to individual needs.
Understanding Gout Attacks and Their Triggers:
Gout episodes are the most common symptom of this ailment, and they are characterized by a sudden onset of intense pain, swelling, and redness in the afflicted joint. The formation of uric acid crystals in the joint is the major cause of gout episodes, which results in an inflammatory reaction by the body’s immune system. A gout attack can be precipitated by a number of reasons, including:
Key Points:
- Dietary Choices: Purine-rich meals, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol consumption can all promote gout flares.
- Dehydration: A lack of fluid consumption might result in greater uric acid levels in the blood, increasing the risk of flares.
- Medical Conditions: Hypertension, obesity, and diabetes can all raise uric acid levels and cause gout episodes.
Duration and Intensity of Flares
Gout flares can vary in duration and intensity from person to person. Gout attacks can continue from a few days to many weeks, with symptoms peaking within the first 24 to 48 hours. Excruciating pain is frequently mentioned, and it may be accompanied by soreness, warmth, and swelling in the afflicted joint. The severity of the pain can make even the most basic motions unpleasant, impairing an individual’s ability to carry out regular tasks.
Key Points:
- Initial Onset: Gout episodes frequently strike unexpectedly and increase quickly within the first day.
- Peak Intensity: Pain and discomfort are generally at their worst in the first 24 to 48 hours.
- Subsiding Symptoms: The symptoms gradually lessen and mobility improves over a few days to weeks.
Impact on Daily Life and Mobility
Gout attacks can have a significant influence on a person’s everyday life and mobility. Excruciating pain and restricted joint movement can make even the most basic actions difficult, such as walking, standing, or holding items. This might result in emotions of irritation, powerlessness, and a worse quality of life. Furthermore, the worry of another flare can cause anxiety and tension, negatively impacting one’s mental well-being.
Key Points:
- Work and Productivity: Gout flares may lead to missed workdays or reduced productivity due to pain and discomfort.
- Physical Limitations: Mobility limitations can hinder participation in physical activities and exercise routines.
- Emotional Well-Being: Persistent pain and limitations can contribute to emotional distress and a reduced sense of well-being.
Expert Tips for Managing Gout Flares
We recognize the difficulties that gout flares provide and are here to offer experienced advice on how to handle them. Here are some helpful hints for dealing with gout attacks:
Important Points:
- Medications: Consult your doctor about the best treatments to relieve pain and inflammation caused by gout flares.
- RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE) Method can help decrease swelling and pain in the afflicted joint.
- Keep Hydrated: Drinking enough fluids will help drain out uric acid and perhaps minimize the intensity of flares.
Treatment of gout:
Acute Gout Treatment: Finding Immediate Relief
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, or NSAIDs, are an essential component of acute gout therapy. These drugs act by lowering inflammation, alleviating pain, and increasing joint function. To relieve the pain associated with gout flares, common NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are frequently recommended. Their anti-inflammatory characteristics assist to reduce pain and swelling in damaged joints, allowing for a speedier recovery.
-
Colchicine
Another important drug for treating acute gout episodes is colchicine. It works by blocking inflammation-causing white blood cells, resulting in immediate relief from gout symptoms. When taken at the earliest sign of an oncoming flare-up, colchicine can significantly decrease pain and inflammation, allowing people to continue their usual activities more easily.
-
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are strong anti-inflammatory medicines that are routinely used to treat severe gout flares, whether orally or intravenously. These drugs relieve pain and swelling immediately, giving patients with much-needed comfort. Although corticosteroids are useful in the short term, they are frequently reserved for situations when NSAIDs or colchicine are ineffective.
Long-Term Management: Sustaining Gout Relief
Adopting some lifestyle adjustments might be beneficial on the route to optimal gout management. A well-balanced diet lacking in purine-rich foods such as organ meats and shellfish will help avoid the buildup of uric acid crystals that cause gout flares. Furthermore, keeping a healthy weight via adequate nutrition and exercise can dramatically lower the incidence of gout episodes, as excess weight is connected with increased uric acid levels.
-
Medications to Lower Uric Acid Levels
Medication targeted at reducing uric acid production or increasing excretion may be administered for those who have recurrent gout episodes or high uric acid levels. Two regularly recommended medicines for this purpose are:
-
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is a medicine that reduces the risk of gout flares by inhibiting the formation of uric acid. It is an important tool in long-term gout care and is frequently administered to people who have a history of repeated episodes.
-
Febuxostat
Like allopurinol, febuxostat is an effective drug that lowers uric acid levels by suppressing its formation. It gives an option for people who cannot take allopurinol or need a different therapeutic method.
The Crucial Role of Patient-Doctor Collaboration
A solid and collaborative connection between patients and their healthcare professionals is vital for the treatment and management of acute gout. Individuals can be guided through the many treatment choices by a skilled and compassionate healthcare provider who considers their medical history, preferences, and lifestyle variables. This teamwork guarantees that the treatment plan adopted is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, boosting the chances of effective gout management and avoiding repeat flares.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Gout, a painful and incapacitating type of arthritis, can have a substantial negative influence on one’s quality of life. Fortunately, lifestyle changes can help to manage gout and reduce the frequency of unpleasant flare-ups. In this detailed guide, we will look at many lifestyle adjustments that can help you control your gout and live a more pleasant life.
Dietary Recommendations: Nourishing Choices for Gout Management
-
Foods to Avoid (High-Purine)
Gout management can be significantly influenced by dietary choices. Purine-rich meals can raise uric acid levels, producing gout flare-ups. Organ meats, shellfish, red meat, and some types of fish are examples of such foods. You may assist reduce the formation of uric acid crystals in your joints by limiting your consumption of these high-purine foods.
-
Foods to Include (Low-Purine)
In contrast, eating low-purine meals can be quite advantageous. Choose lean proteins like chicken, tofu, and lentils. Whole grains, fruits and vegetables, and low-fat dairy products are all good options. These nutrient-dense meals not only promote general health but also help to reduce uric acid levels, lowering the likelihood of gout attacks.
-
Hydration: The Role in Uric Acid Regulation
Gout management requires enough hydration. Staying hydrated allows your body to more efficiently drain away excess uric acid, lowering its content in your bloodstream. Drink lots of water throughout the day to help with uric acid control and reduce the probability of gout flare-ups.
-
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and living an active lifestyle can help with gout control substantially. Physical activity aids in weight control, joint function, and overall well-being. Low-impact workouts like swimming, walking, and yoga can be especially useful for people with gout since they reduce joint stress while increasing flexibility and strength.
-
Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact
Alcohol use can have a variety of effects on gout. Because of their purine content, beer, and spirits, in particular, have been linked to an elevated risk of gout flares. Furthermore, alcohol might obstruct the excretion of uric acid from the body, worsening the illness. While moderate wine drinking may have a less dramatic effect, alcohol consumption should be limited to avoid gout-related problems.
Proactive Prevention Strategies for Long-Term Gout Relief
Gout prevention is a multidimensional endeavor that needs to recognize risk factors and apply interventions to limit their influence. By taking a proactive approach, you may lessen the frequency and severity of gout episodes, allowing you to live a more meaningful and pain-free life.
-
Identifying and Addressing Risk Factors
Understanding the causes of gout is vital for successful prevention. Gout risk is increased by genetic susceptibility, obesity, high blood pressure, and certain medical disorders. You may make educated decisions about your lifestyle and treatment options if you recognize these risk factors and engage with your healthcare professional to address them.
Obesity is strongly connected to the onset of gout. Excess weight can raise uric acid levels, increasing the risk of gout flares. You may reach and maintain a healthy weight by following a balanced food plan and engaging in regular physical exercise, lowering the load on your joints and minimizing gout-related suffering.
-
Regular Monitoring and Management of Uric Acid Levels
Uric acid levels must be monitored regularly to prevent gout. Your doctor can do blood tests to determine your uric acid levels and change your treatment plan accordingly. You can successfully lower the likelihood of gout episodes and their accompanying symptoms by maintaining appropriate uric acid levels.
-
Role of Medication in Preventing Recurrent Attacks
Medication may play an important role in prevention for people who have frequent gout episodes or high uric acid levels. To reduce uric acid production, your doctor may prescribe drugs such as allopurinol or febuxostat. These drugs, when paired with lifestyle changes, can reduce the probability of gout flares and support long-term gout treatment.
Potential Complications of Gout:
Gout, an inflammatory disease, can cause a variety of consequences that impair numerous aspects of health. In this part, we will look at probable gout complications and techniques for dealing with them.
-
Chronic Gout and Tophi Formation
Chronic gout develops when gout flares become frequent and chronic, resulting in the formation of tophi – deposits of uric acid crystals beneath the skin. Tophi may cause joint abnormalities as well as persistent pain and suffering. Early and effective gout care is critical for preventing chronic gout development and reducing the incidence of tophi formation.
-
Kidney Stones and Renal Complications
Uric acid can crystallize not just in joints but also in the kidneys, resulting in the production of kidney stones. These stones can cause extreme discomfort and, in severe cases, kidney damage. Individuals with gout are more likely to develop kidney stones, emphasizing the need for good gout care in lowering this risk and protecting renal function.
-
Joint Damage and Deformities
Gout, if left untreated or poorly managed, can cause joint damage and abnormalities. Uric acid crystal buildup can cause chronic inflammation and joint tissue degradation. This procedure may result in joint abnormalities and impaired joint function. Adherence to gout treatment programs and early intervention are critical for protecting joint health and preventing long-term harm.
Gout: Coping and Thriving Strategies
Living with gout entails not only dealing with physical symptoms but also dealing with the emotional and psychological effects of the disorder. In this section, we will look at ways for dealing with gout-related issues and improving general well-being.
-
Managing Pain and Flares
Gout flare-ups can be excruciatingly painful and inconvenient. Pain management during flares necessitates a combination of rest, medicine, and lifestyle changes. Applying ice to the injured joint, elevating it, and taking prescription drugs as instructed will help relieve pain. Additionally, working together with your healthcare physician to build a personalized pain management strategy is critical for efficiently navigating gout flares.
-
The Psychological and Emotional Consequences
Living with a chronic illness, such as gout, can have serious psychological and emotional consequences. The unpredictability of flares, restrictions on physical activity, and fears of future difficulties can all contribute to stress, worry, and even melancholy. Seeking help from mental health specialists and joining support groups can be beneficial in coping with the emotional elements of living with gout.
-
Networks of Support and Resources
Individuals suffering from gout must develop a strong support network. Connecting with individuals who have gone through similar things can give you a sense of belonging and understanding. Online networks, local support groups, and patient advocacy organizations all provide venues for people to share their experiences, advice, and encouragement. These tools can be quite helpful in navigating the difficulties of living with gout.
Diet for gout:
- Hydration: Drink water to flush out uric acid.
- Limit Purines: Reduce red meat, organ meats, and shellfish.
- Lean Protein: Choose poultry, tofu, and low-fat dairy.
- Complex Carbs: Opt for whole grains, fruits, and veggies.
- Cherries & Berries: Enjoy anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Limit Sugar & Alcohol: Cut sugary drinks and excessive alcohol.
- Healthy Fats: Use olive oil, nuts, and avocados.
- Vitamin C Foods: Consume citrus fruits and peppers.
- Portion Control: Maintain healthy weight.
Gout Research Advances and the Future
As medical knowledge advances, current research in gout therapy and management holds the possibility of better results for people who suffer from the ailment. We investigate the present status of gout research and its possible influence on future medicines in this article.
-
Gout Treatment and Management Research is ongoing
Researchers are always looking at novel approaches to gout therapy and management. Understanding the underlying processes of gout, discovering novel therapeutic targets, and optimizing current therapy are all priorities in research. Keeping up with the newest scientific discoveries can help individuals and healthcare professionals make educated decisions about gout therapy.
-
Potential Medical Breakthroughs and Novel Therapies
Medical research advancements have the potential to result in novel gout therapy. The future promises promise for more effective and personalized treatment choices, from targeted medication therapy to sophisticated surgical methods. Individuals with gout can get the best care possible by staying involved with healthcare specialists and updated about new medications.
-
The Importance of Raising Public Awareness and Knowledge
Raising public awareness of gout is crucial for expanding understanding, removing stigma, and encouraging early detection and treatment. Education initiatives, community activities, and online resources can all help to dispel gout beliefs and encourage proactive management. We can improve the well-being and quality of life of gout patients by working together to increase knowledge and awareness.
Pseudo gout:
Pseudo Gout, also known as calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), occurs when calcium crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. It often resembles gout in symptoms, such as sudden pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint, including the hand. Pseudo Gout typically affects larger joints, like the knee, but can also target smaller joints like those in the hands.
Gout in hands:
It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. The hand, particularly the finger joints and wrist, can be affected. Gout attacks lead to intense pain, swelling, and warmth in the joint. The skin around the joint might appear red and shiny. Gout flares often come on suddenly and can be triggered by factors like diet, alcohol consumption, and genetics.
Managing both conditions involves lifestyle changes, medications, and targeted treatments. If you suspect you have Pseudo Gout or gout in your hand, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on managing your symptoms effectively.
Conclusion: Empowering Gout Management and Raising Awareness
We’ve covered the fundamentals of gout – inflammatory arthritis characterized by uric acid crystals in joints – in this detailed tutorial. Let us review the main themes, emphasize proactive management, and promote ongoing education.
Gout is characterized by painful flare-ups caused by uric acid crystal accumulation. NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids provide immediate relief. Long-term approaches include dietary changes, exercise, and drugs such as allopurinol.
-
Proactive Gout Management
It is critical to take action as soon as possible. Address risk factors, maintain a healthy weight, remain hydrated, and work with healthcare providers. Proactive measures minimize flare frequency and improve overall well-being.
-
Seeking Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare practitioner for personalized care. Talk about your symptoms, concerns, and treatment preferences. Their advice improves gout management.
-
Fueling Education and Awareness
Understanding gout allows you to make educated decisions. Recognize symptoms, get prompt treatment, and eradicate stigmas. Raising public awareness benefits persons suffering from gout.
To summarise, proactive gout management is essential. Engage healthcare providers, embrace education, and refute myths. We are working together to raise gout awareness to enhance people’s lives.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding Symptoms, Treatment, and Management


