If you enjoy high-intensity interval training (HIIT), you already know that it’s a fantastic exercise for shedding pounds and gaining muscle. But did you realize that the quality of your diet can significantly affect how effective your HIIT workouts are? This piece will discuss how to develop a nutrition strategy that works in tandem with your HIIT workouts to help you reach your fitness objectives.
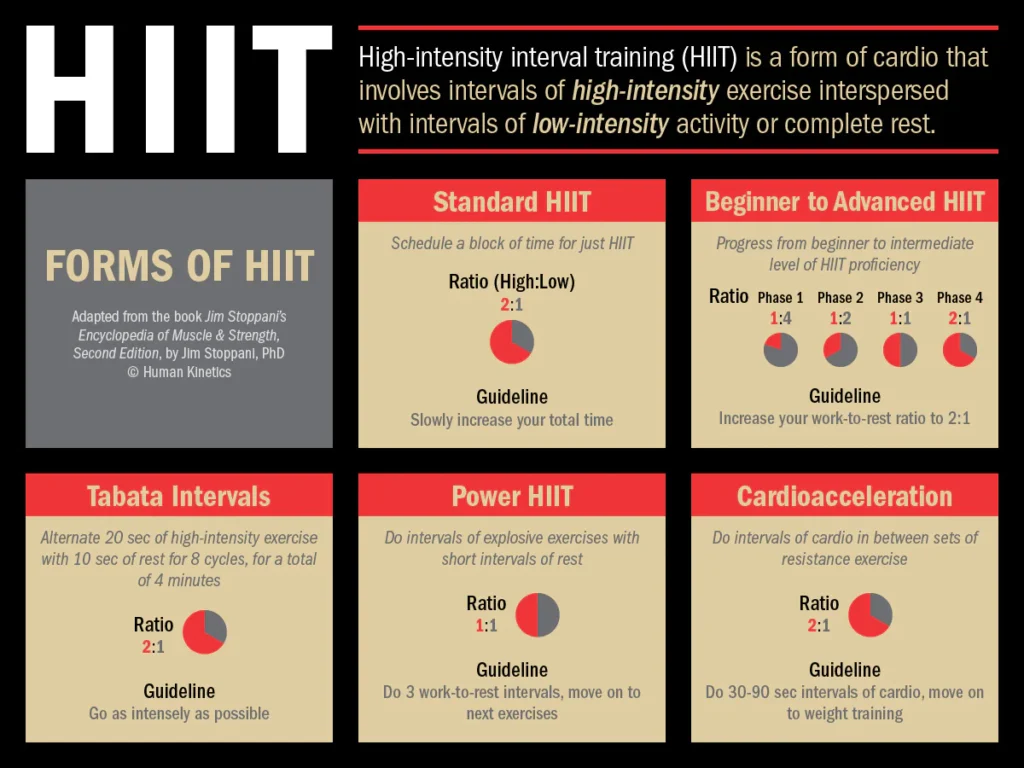
Recognizing HIIT Exercises:
Let’s go over what HIIT workouts are and why they are so successful before getting into the nutrition plan. A workout called HIIT varies between brief bursts of high-intensity activity and rest or low-intensity activity. The goal is to exert maximum effort on your body during high-intensity intervals, which can speed up your metabolism and aid in calorie burning throughout the day.

The Value of Nutrition Before Exercise:
It’s essential to fuel your body correctly before exercise to get the most out of your HIIT workouts. You can get the energy you need for your exercise by eating a small meal or snack that includes both protein and carbohydrates between 30 and an hour prior to starting. A hard-boiled egg and a slice of toast, a banana with almond butter, or a protein shake with fruit are all excellent pre-workout snacks.
Nutrition Prior to Workout: Prepare Your Body for HIIT:
It’s crucial to eat a balanced meal that gives your body the energy it requires prior to beginning your HIIT workout. Here are some suggestions for pre-workout meals to help you feed your body and achieve your best performance:
Oatmeal with fruit: Oatmeal with fruit, such as berries or bananas, is a great source of complex carbohydrates that will give you the energy that lasts all the way through your exercise.
Greek yogurt with nuts and fruits: Greek yogurt is rich in protein, which is necessary for muscle repair and recovery. You can boost your energy level for your exercise by mixing nuts and fruits into your yogurt.
Smoothies: Smoothies are a great choice for a fast and simple pre-workout meal. Making a smoothie with spinach, banana, berries, and Greek yogurt is a tasty and healthy way to fuel your body for peak performance.

Water intake during HIIT workouts:
For optimum performance, it’s also important to stay hydrated throughout your HIIT exercise. To keep your body hydrated throughout your workout, make sure to consume plenty of water before, during, and after. You might also want to think about drinking an electrolyte drink to replace the minerals lost through perspiration if your HIIT exercise is especially strenuous or prolonged.
Post-Workout Nutrition:
There must be refuel your body with the nutrients it requires to recover and build muscle after your HIIT workout. Within 30 to 60 minutes of working out, consume a breakfast or snack that includes both protein and carbohydrates to aid in muscle recovery and regrowth. Protein shakes with fruit, turkey, and cheese sandwiches on whole-grain bread, and Greek yogurt with cherries are all tasty post-workout snacks.
To ensure optimum recovery following your HIIT exercise, it’s crucial to refuel your body with the appropriate nutrients. Here are some suggestions for post-workout meals to aid in your recovery and refueling.
Chicken and sweet potato: After working out, your muscles will need to be repaired and replenished. Grilled chicken and sweet potatoes are excellent forms of protein and complex carbohydrates.
Quinoa and veggies: Quinoa is a complete protein that is also rich in fiber and complex carbohydrates veggies will give your body the vitamins and minerals needed, such as spinach or broccoli.
Protein shakes: These are a great choice for a fast and simple post-workout supper. Create a delectable and nourishing shake with protein powder, almond milk, and fruits to aid in your recovery and refueling.


The Function of Macronutrients in the HIIT Diet:
It is important to be aware of the foods you’re consuming in addition to planning your meals and snacks around your workouts. Protein, carbohydrates, and fat, which are all macronutrients, are crucial for HIIT exercise fuel and recovery.
Protein
Protein is necessary for the development and maintenance of muscle structure. Every meal and snack should contain a source of protein, such as lean meats, eggs, dairy foods, legumes, or nuts.
Carbohydrates
The primary fuel source for the body is carbohydrates, which give you the energy you need to complete your HIIT exercises. Instead of easy carbohydrates like sugar and refined grains, choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Fats
Fats are crucial for supplying energy and assisting with muscular recovery. Healthy fats, like those in nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish, are a good source of these nutrients.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, like vitamins and minerals, are also crucial for maintaining general health and performance during HIIT workouts in addition to macronutrients. For the HIIT diet, some important micronutrients are:
Iron: Helps muscles receive oxygen for optimum efficiency. Lean red meat, poultry, seafood, beans, and fortified cereals are all excellent options.
- Calcium: Vital for the well-being of bones and muscles. Leafy greens, dairy products, and fortified plant milk are all excellent options.
- Vitamin D: Aids in calcium absorption and immune system support. Fatty seafood, fortified foods, and adequate sunlight are all good sources.
- Magnesium: Vital for proper nerve and muscle activity. Nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy greens are excellent options.
Nutritional supplements for HIIT:
Although eating whole foods is always preferred, some people may gain from taking supplements to support their HIIT diet. Typical HIIT nutrition additives include:
For vegetarians and vegans in particular, protein powder is a convenient method to increase protein intake.
- Creatine: During HIIT workouts, creatine may enhance muscle and power.
- Caffeine: Can improve energy levels and HIIT workout efficiency.
- Beta-alanine: This can assist during HIIT workouts to increase endurance and postpone muscle fatigue.
Avoiding Certain Foods Before HIIT Workout:
While many foods can help you fuel your HIIT exercises, there are some that you should stay away from before working out. During HIIT workouts, the following foods may slow you down or create digestive discomfort:

Food to avoid - Foods high in fat: Slow to process and cause discomfort while exercising.
- Spicy foods: This may result in indigestion or reflux.
- Foods high in fiber: may result in flatulence or bloating.
- Sugary foods: These can cause blood sugar levels to increase and fall quickly, leaving you feeling exhausted.

HIIT Nutrition Plan Sample:
Here is an example HIIT nutrition strategy for a day of vigorous exercise to tie everything together:
- Pre-workout snack: Banana with almond butter.
- During workout: Water or electrolyte drink.
- Post-workout snack: Protein shake with fruit.
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and granola.
- Snack: Apple with almond butter.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, veggies, and quinoa.
- Snack: Hard-boiled egg with carrot sticks.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with sweet potato and roasted veggies.
- Dessert: Dark chocolate and berries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, putting together a nutrition plan to go along with your HIIT exercises can help you accomplish your fitness objectives more quickly. You can fuel your body effectively for the best performance and recovery by planning your meals and snacks around your workouts and being mindful of your macronutrient and micronutrient consumption.
FAQs:
- Can I perform HIIT exercises when I’m hungry?
It’s not advisable to perform HIIT exercises on an empty tummy because you might lack the energy needed to complete the exercise. Before working out, having a modest meal or snack that contains both protein and carbohydrates can help you get the energy you need.
-
Are vitamins required for HIIT nutrition?
While eating whole foods is always preferred, some people may gain from taking supplements to support their HIIT diet. Before ingesting any drugs, seek medical advice.
-
What are some excellent protein sources for HIIT diets?
Lean meats, eggs, dairy products, beans, and lentils are all excellent forms of protein for HIIT diets.



2 Comments on “Nutrition Plan for HIIT Workouts:”